What Is an EV Charger? The Ultimate Guide With 7 Powerful Insights for Beginners
What Is an EV Charger?
Introduction to Electric Vehicle Charging
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular every year as people look for cleaner, more cost-effective ways to travel. With this growing demand comes an important question many beginners ask: what is an ev charger and how does it work? Understanding this basic yet essential component is the first step toward owning and operating an electric vehicle with confidence.
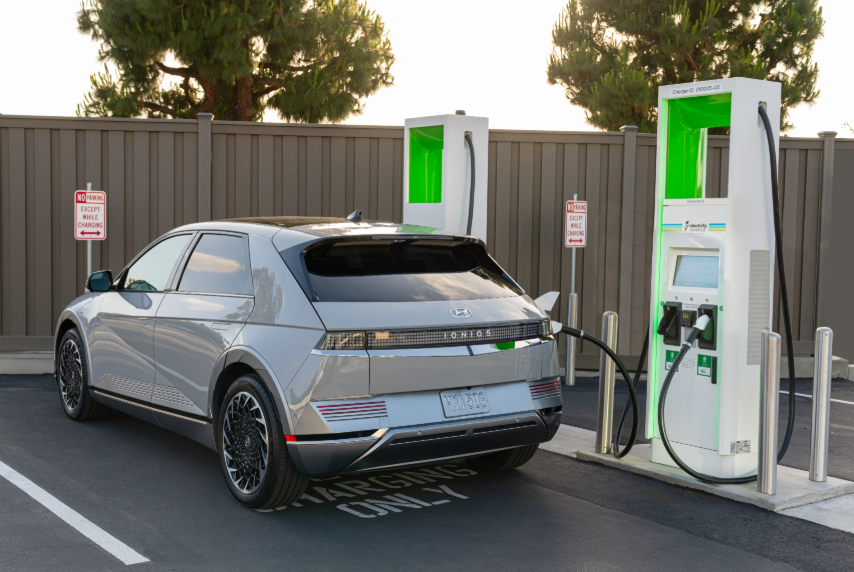
An EV charger is more than just a plug. It is a device that safely delivers electricity from a power source to an electric vehicle’s battery. Without it, EVs simply cannot operate. As governments push toward lower emissions and car manufacturers release more electric models, EV chargers are quickly becoming a part of everyday life in homes, workplaces, and public spaces.
What Is an EV Charger and Why It Matters
So, what is an ev charger exactly? An EV charger is specialized equipment designed to supply electrical energy to recharge an electric vehicle’s battery. Unlike fueling a gasoline car, EV charging requires controlled electricity flow to protect both the vehicle and the user.
EV chargers matter because they:
- Enable convenient and reliable vehicle charging
- Protect batteries from overloading or overheating
- Support faster charging speeds compared to standard outlets
- Make electric vehicle ownership practical and efficient
Without EV chargers, electric vehicles would be limited, slow to recharge, and unsafe to operate. They are the backbone of the EV ecosystem and a critical part of clean transportation infrastructure.
See also: Decoding Video DRM: Essential Points for Content Security
How an EV Charger Works
EV chargers operate using advanced electrical and communication systems to ensure safe energy transfer.
Power Source and Electricity Flow
An EV charger draws electricity from a power source, such as a home electrical panel or a public grid. The charger regulates voltage and current before sending power to the vehicle. This controlled flow prevents electrical damage and ensures efficient charging.
Role of the Charging Cable and Connector
The charging cable connects the EV charger to the vehicle. It contains insulated wires and safety features that handle high electrical loads. The connector at the end must match the vehicle’s charging port to establish a secure connection.
Communication Between Car and Charger
Modern EV chargers communicate digitally with the vehicle. This communication allows the charger to:
- Identify battery capacity
- Adjust charging speed
- Stop charging when the battery is full
- Detect faults or overheating
This smart interaction is what makes EV charging safe and reliable.
Types of EV Chargers Explained
Understanding charger types helps answer the broader question: what is an ev charger used for in different situations?
Level 1 EV Chargers
Level 1 chargers use a standard household outlet (120V). They are slow but convenient and require no special installation.
Key features:
- Adds about 3–5 miles of range per hour
- Best for overnight charging
- Lowest cost option
Level 2 EV Chargers
Level 2 chargers operate at 240V and are common in homes and public locations.
Key features:
- Adds 20–40 miles of range per hour
- Requires professional installation
- Ideal for daily charging needs
DC Fast EV Chargers
DC fast chargers are used mainly in commercial and highway locations.
Key features:
- Can charge 80% in 20–40 minutes
- Uses direct current (DC)
- Higher cost and power demand
EV Charger Connector Types
Not all EV chargers use the same connectors.
Type 1 and Type 2 Connectors
- Type 1: Common in North America
- Type 2: Standard in Europe and many other regions
CCS and CHAdeMO
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Widely adopted for fast charging
- CHAdeMO: Older fast-charging standard, still in use
Tesla Charging Connectors
Tesla vehicles use proprietary connectors, though adapters allow compatibility with other EV chargers.
Home EV Chargers vs Public EV Chargers
Benefits of Home EV Charging
Home EV chargers offer unmatched convenience.
Advantages include:
- Charging overnight
- Lower electricity costs
- No waiting lines
- Increased property value
Public Charging Stations Overview
Public EV chargers are found at malls, offices, highways, and parking lots. They provide flexibility for long trips and drivers without home chargers.
You can explore public charging networks at https://www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles.
How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV?
Charging time depends on:
- Charger type
- Battery size
- Current battery level
| Charger Type | Average Charging Time |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | 8–20 hours |
| Level 2 | 4–8 hours |
| DC Fast | 20–40 minutes |
Cost of EV Chargers and Installation
EV Charger Equipment Costs
- Level 1: Often included with vehicle
- Level 2: $400–$1,200
- DC Fast: $10,000+
Installation and Maintenance Costs
Installation costs vary depending on electrical upgrades and location, typically ranging from $300 to $2,000 for home chargers.
Safety Features of EV Chargers
EV chargers include built-in protections such as:
- Overcurrent protection
- Ground fault detection
- Automatic shut-off
- Weatherproof casing
These features ensure user safety and equipment durability.
Environmental Benefits of EV Charging
Using EV chargers helps reduce:
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Air pollution
- Dependence on fossil fuels
When paired with renewable energy, EV charging becomes even more sustainable.
Smart EV Chargers and Future Technology
Smart EV chargers allow users to:
- Schedule charging during off-peak hours
- Monitor energy usage via apps
- Integrate with solar panels
- Participate in grid balancing
The future of EV charging includes wireless charging and ultra-fast systems.
Common Myths About EV Chargers
- Myth: EV chargers are unsafe
Fact: They are highly regulated and tested - Myth: Charging always takes hours
Fact: Fast chargers significantly reduce time - Myth: EV chargers damage batteries
Fact: Smart chargers protect battery health
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an ev charger used for?
An EV charger is used to safely recharge an electric vehicle’s battery using controlled electricity.
2. Can I install an EV charger at home?
Yes, most homeowners can install a Level 2 EV charger with professional help.
3. Are EV chargers expensive to run?
No, charging an EV is generally cheaper than fueling a gasoline car.
4. Do all EV chargers work with every car?
Not always. Connector types and charging standards must be compatible.
5. Is it safe to charge an EV in the rain?
Yes, EV chargers are designed to be weather-resistant and safe.
6. How long do EV chargers last?
Most EV chargers last 10–15 years with proper maintenance.
Conclusion
Understanding what is an ev charger is essential for anyone interested in electric vehicles. EV chargers make clean transportation possible by delivering safe, efficient, and reliable energy to electric cars. With various charger types, smart technology, and growing infrastructure, EV charging is easier and more accessible than ever. As electric vehicles continue to shape the future of mobility, EV chargers will remain at the heart of this transformation.